Description
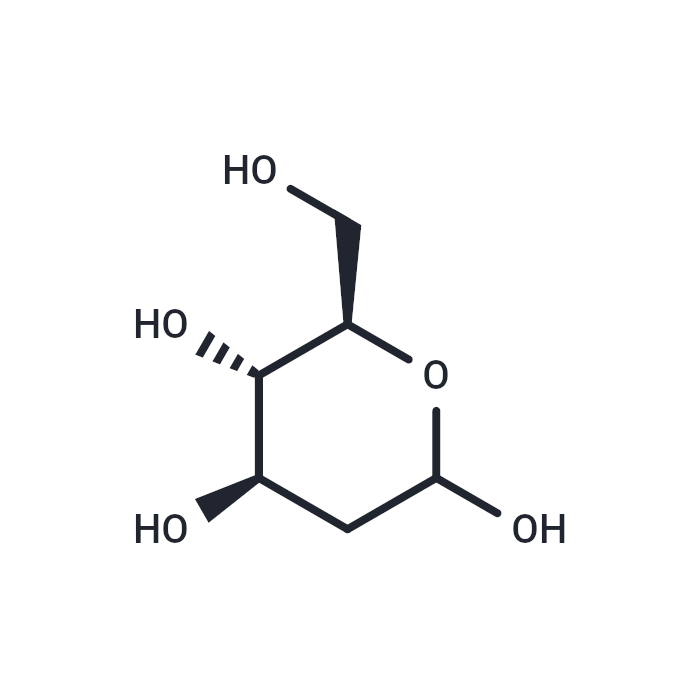
2-Deoxy-D-glucose (2-DG), 500g
(Synonyms: 2-Deoxyglucose, 2-Deoxy-D-arabinohexose, 2-DG)
is a non-metabolizable glucose analogue that disrupts glycolysis by inhibiting hexokinase, the key regulatory enzyme in this metabolic pathway. When hexokinase phosphorylates 2-DG, it converts it into 2-DG-P, leading to its accumulation within the cell and resulting in a depletion of cellular ATP levels. This mechanism is particularly effective in targeting and eliminating cancer cells by depriving them of energy. Additionally, 2-DG may also hinder viral replication in cells that depend on glycolysis for their energy needs.
Furthermore, 2-DG is utilized in glucoprivic feeding research to invoke and study the processes of counter-regulatory response (CRR). It also plays a role in the development of anti-cancer strategies that involve radio- and chemosensitization, as well as the induction of oxidative stress. This multifunctional compound finds applications across various fields, including cancer research, virology, metabolomics, and biochemical studies.
More
Publications: PubMed
Certificates: COA